- TOOL KITS
- A. The NEXT Step
- B. Promoting Independence
- C. Phone Apps
- D. Return to Work
- E. Motivational Interviewing
- F. Paediatric Brain Injury Rehabilitation Resources
- a) Introduction
- 0. Introduction
- 1. Transition
- 2. The transition wheel
- 3. Walking around the transition wheel
- 4. The transition wheel interview
- 5 . Using this kit
- 6 . Web resources
- b) Working together
- 7. My role
- 8 . My family's role
- 9. My case manager's role
- c) What can I do?
- 10. Who, where, what? The Services I receive
- 11. Accommodation
- 12. Driving
- 13.Alcohol and drugs
- 14. Social and recreational activities
- 15. Health and well-being
- 16. Relationships and friendships
- 17. Sexuality
- 18. Personal safety
- 19. Complaints/rights
- 20. Legal issues
- 21. Centrelink
- 22. Financial
- 23. Shopping
- 24. Employment, training and tertiary education
1. Transition
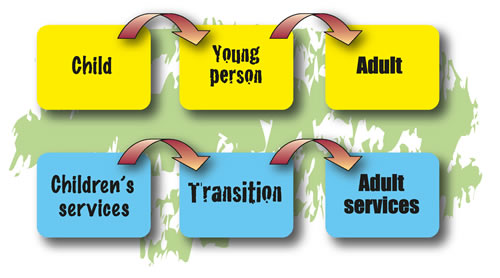
As everyone matures from childhood to adulthood they have to change from using children’s services to using adult services.
Changing to adult services involves young people in saying goodbye to the people who helped you in the children's services. This can be difficult and scary, especially if they have known them for a long time.
Transition is the planned move from services for children and young people to services for adults.
During the time of transition, the young person may start to make new contacts and relationships with the workers of adult services such as doctors, case manager or other therapists. This starts the process of building up confidence with using new adult services.
Every adolescent, as they get older will become more independent. They will want to do more and more things for themselves. They will not need their family as much as they do when they are younger.
Adult services require the young person to be more independent. People working with the young person will ask them directly about their opinions. Their case manager, rehabilitation staff and doctor will start asking them to make decisions about their lives. They will not always ask their parents.
In transition from children's services to adult services young people need to become more independent, for example:
- Learning to pick out their own clothes to wear
- Learning to dress themselves
- Learning to cook
- Learning to clean their house
- Learning how to catch a bus or a train
- Learning how to do the shopping
- Learning about their brain injury
- Talk with their doctor without their parents present
In adult services young people will have the opportunity to talk talk about things they have never talked about before. These may include issues such as sexuality, drugs and alcohol and birth control. These are all important issues that they will need to know about as they become adults.
Changing to adult services involves young people in saying goodbye to the people who helped you in the children's services. This can be difficult and scary, especially if they have known them for a long time. They may need to start seeing a doctor, case manager, or other therapists at an adult services and start to build up confidence in them.

