- SELF STUDY MODULES
- 1. Intro to TBI
- 2. Communication
- 3. Skills for independence
- 4. Cognitive changes
- 5. Behaviour changes
- 6. Sexuality
- 7. Case management (BIR)
- 8. No longer available
- 9. Mobility & motor control
- 10. Mental health & TBI:
an introduction - 11. Mental health problems
and TBI: diagnosis
& management - 12. Working with Families
after Traumatic Injury:
An Introduction - 13. Goal setting
- 2.0 Aims
- 2.0A Take the PRE-Test
- 2.1 Communication
- 2.2 Sources of ommunication difficulties
- 2.3 Communication Problems
a) Dysphasia
b) Dysarthria
c) Dyspraxia
d) Non-verbal
AAC - 2.4 Cognitive problems
- 2.5 Social communication deficits
- 2.6 Tips for talking
- 2.7 Take home messages
- 2.8 Resources
- 2.9 Take the POST-Test
2.2 Sources of communication difficulties
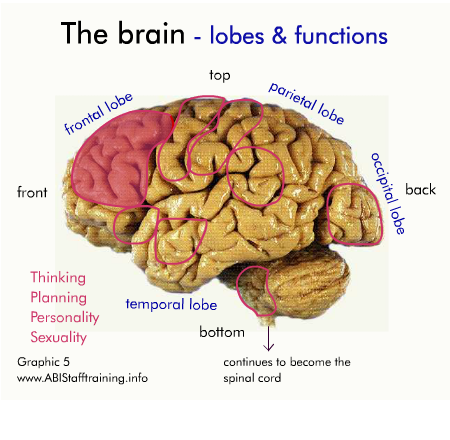
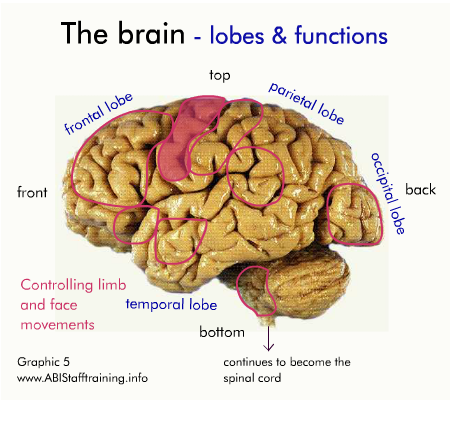
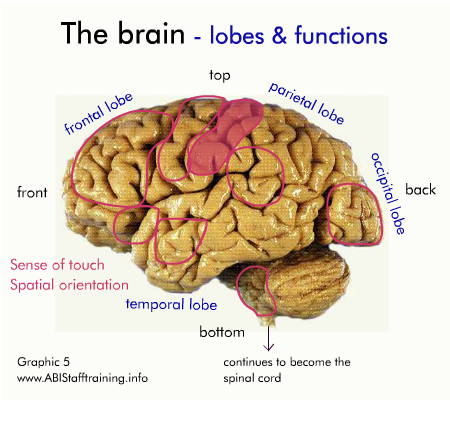
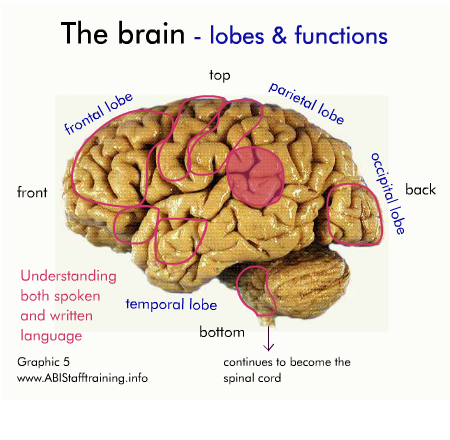
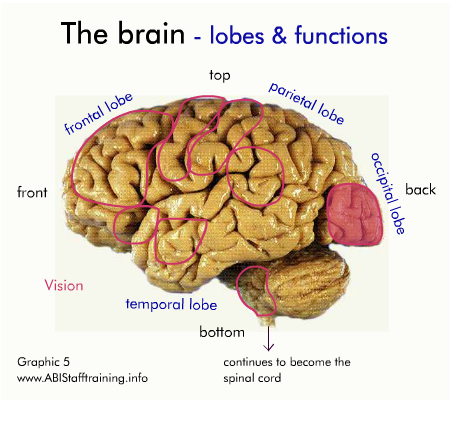
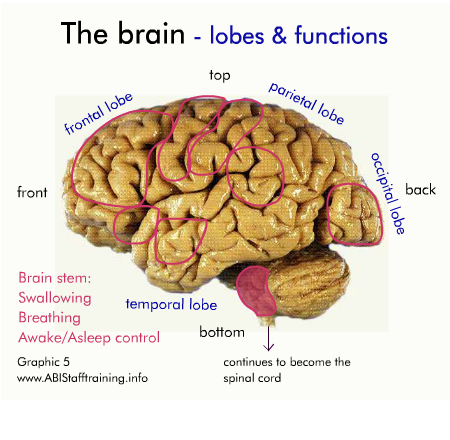
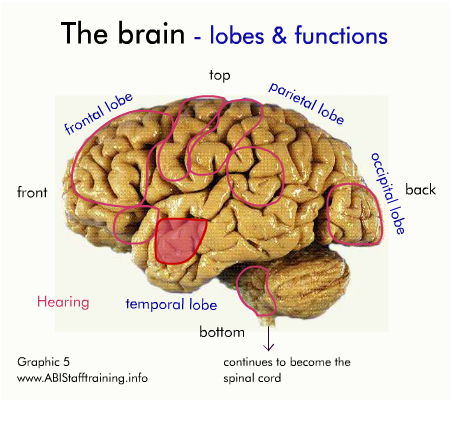
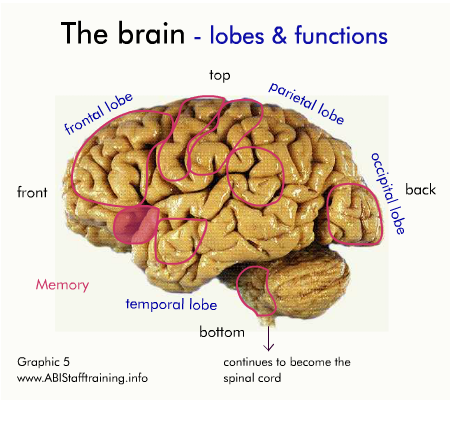
The brain and communication
The following diagram shows the physical areas of the brain and the associated functions.
Click on the diagram to activate it.
For each area of the brain, think about how damage to the area might affect communication.
If you have already completed Module 1 Introduction to Traumatic Brain Injury you can go to the next section 2.3 Experience - what its like to have a communication problem.
SLIDES: To pause: Hover mouse over slide. To continue: move mouse off slide.
To go to a specific slide: Click on slide numbers below.
For further detail on the anatomy of the brain see Module 1.3 Anatomy