- SELF STUDY MODULES
- 1. Intro to TBI
- 2. Communication
- 3. Skills for independence
- 4. Cognitive changes
- 5. Behaviour changes
- 6. Sexuality
- 7. Case management (BIR)
- 8. No longer available
- 9. Mobility & motor control
- 10. Mental health & TBI:
an introduction - 11. Mental health problems
and TBI: diagnosis
& management - 12. Working with Families
after Traumatic Injury:
An Introduction - 13. Goal setting
- 10.0 Aims
- 10.0A Take the PRE-Test
- 10.1 Mental health & mental illness
- 10.2 Why identify mental health problems after TBI
- 10.3 Why a person might get a mental health problem
- 10.4 The brain and mental health problems
- 10.5 Types of mental health problems after a TBI
- a) Depression
- b) Psychosis
- c) Anxiety
- d) Personality change
- 10.6 Fatigue and problems initiating activities
- 10.7 Issues in using:
- a) Drugs & alcohol
- b) Pain killers
- c) Natural therapies
- 10.8 Treatment challenges
- 10.9 Who to see - services available
- 10.10 Take home messages
- 10.11 Resource
- 10.12 Take the POST-test
10.1 Mental health,mental illness and TBI
Q in the heading indicates there are self test questions on the page
- i)
Intro - ii) Mental
health - iii) Mental
illness - iv) Mental health
problems - v) A person's
abilities - vi) A person's
lifespan -
vii)
Rehabilitation Q
Introduction
To set the scene for working on mental health problems in traumatic brain injury it is useful to:
-
Understand what is meant by mental health
-
Understand what is meant by mental illness
-
Be aware of a person's abilities and see the areas in which mental health problems impact on a person
-
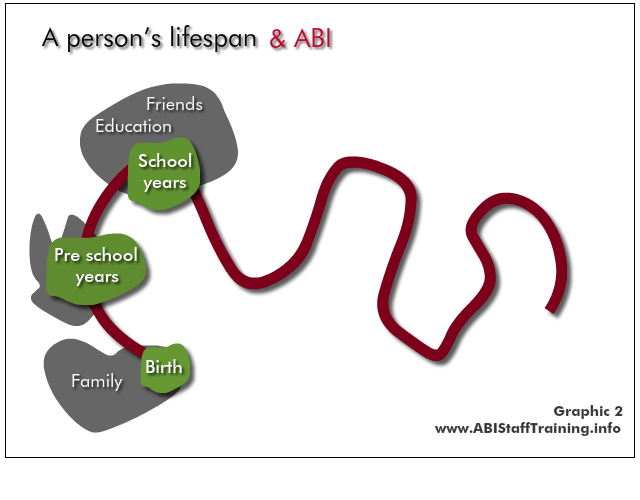
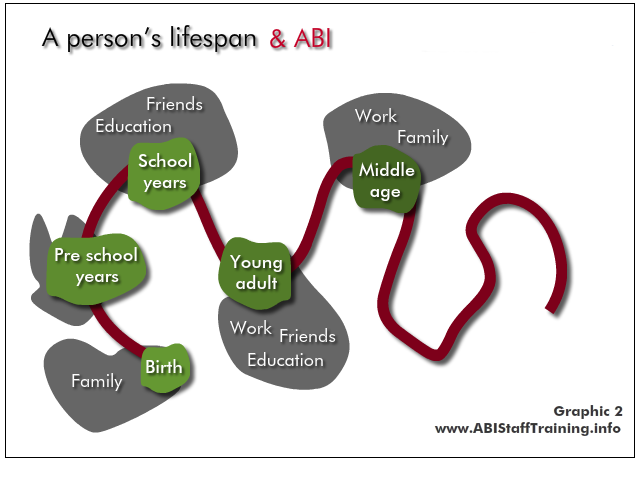
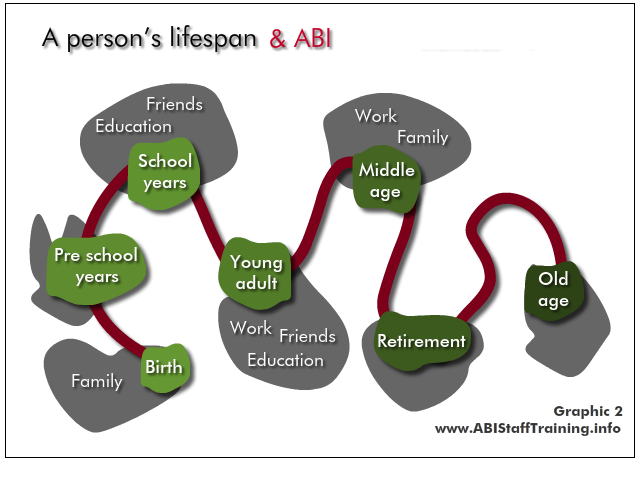
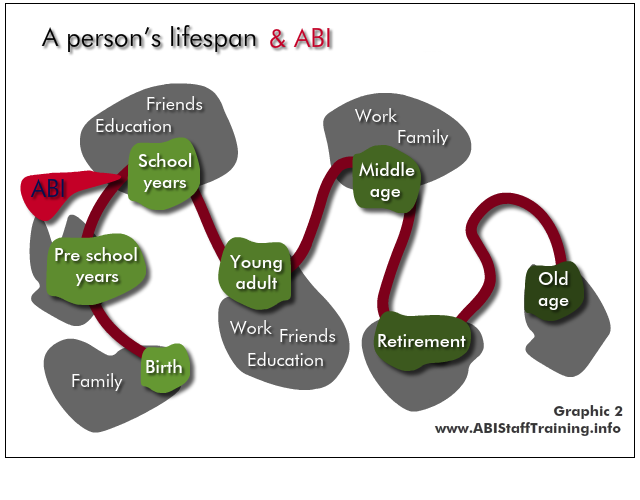
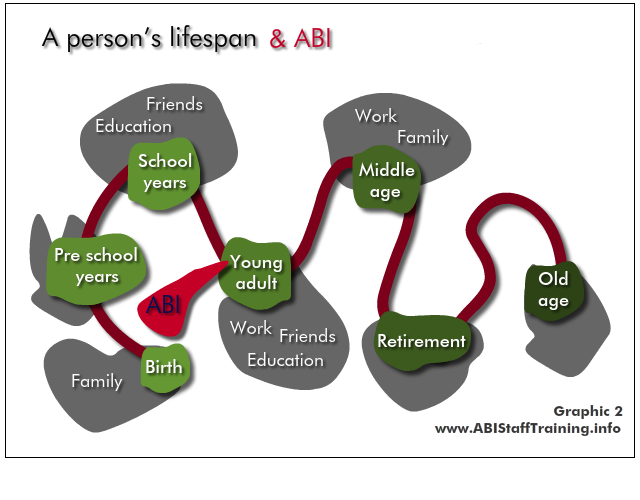
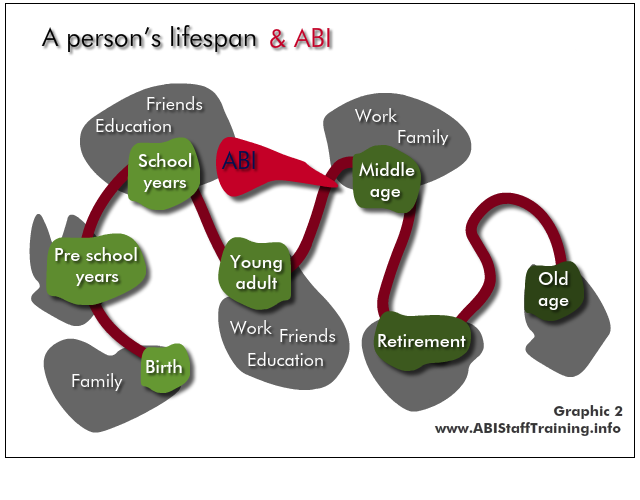
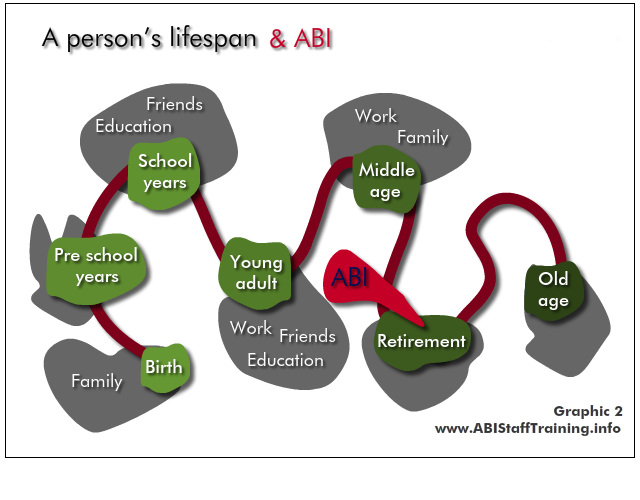
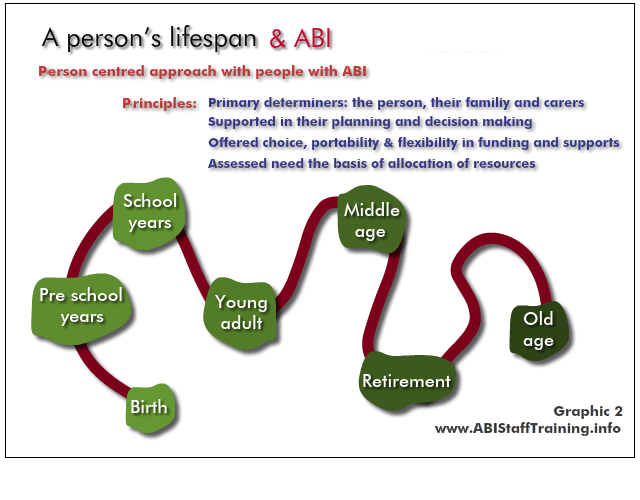
See the person in the content of their whole lifespan - what has come before? At what point are they in their life? What is yet to come?
-
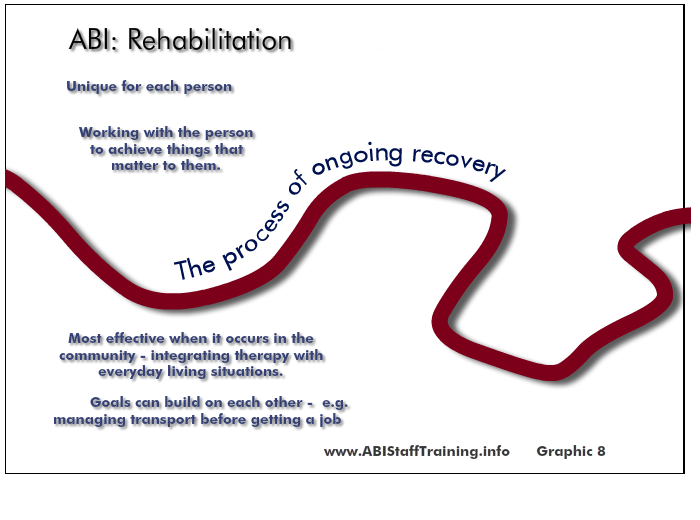
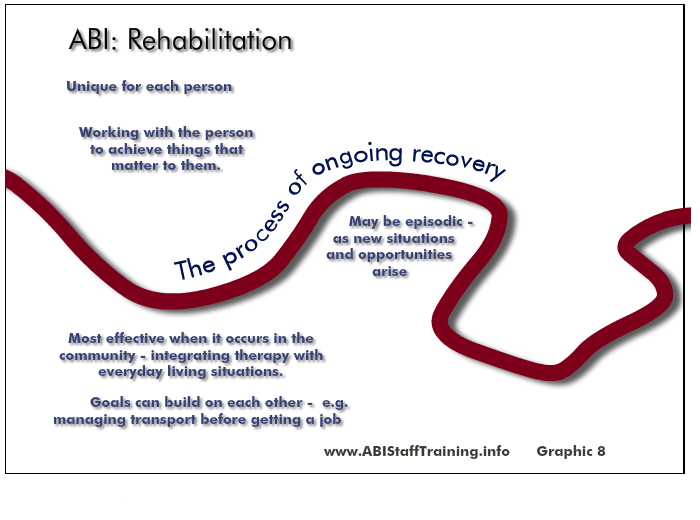
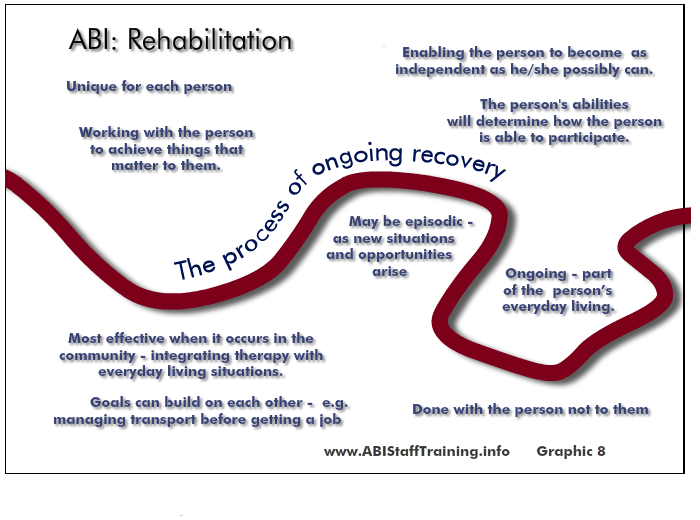
Be aware of the process of rehabilitation that a person with traumatic brain injury will be part of.
Mental health
Mental health is sometimes defined as an absence of mental illness.
It is better to describe it as the person having particular ways of thinking or behaviour that help them to feel good and to maintain how they feel on a daily basis.
The World Health Organisation (WHO) states: "Mental health is an integral and essential component of health."
The WHO constitution states: "Health is a state of complete physical, mental and social well-being and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity." An important consequence of this definition is that mental health is described as more than the absence of mental disorders or disabilities.
Mental health is a state of well-being in which an individual realizes his or her own abilities, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and is able to make a contribution to his or her community. In this positive sense, mental health is the foundation for individual well-being and the effective functioning of a community.
Reference: World Health Organisation
Mental illness
Typically, we talk about mental health problems or mental illness, there is no good definition, and the concept of mental illness can be subjective and culture bound.
We define a person as having a particular mental illness if they have symptoms or behaviour that typically represents syndromes of behaviour that psychiatrists or psychologists may diagnose as a “mental illness”.
A mental illness can result in a disruption in a person's thinking, feeling, moods, ability to relate to others, and behaviour. Mental illness can be defined by legislation, although each state and country will have slightly different legislation.
In this module we are defining mental illness as a person:
- having particular symptoms or behaviour
- that represents certain types of illnesses that psychiatrists or psychologists diagnose according to common diagnostic criteria.
Types of mental health problems after a traumatic brain injury
Types of mental health problems after a traumatic brain injury include:
a) Depression
b) Psychosis
c) Anxiety disorders, including posttraumatic stress disorder
d) Personality change
Each of these can be diagnosed by a psychiatrist or psychologist.
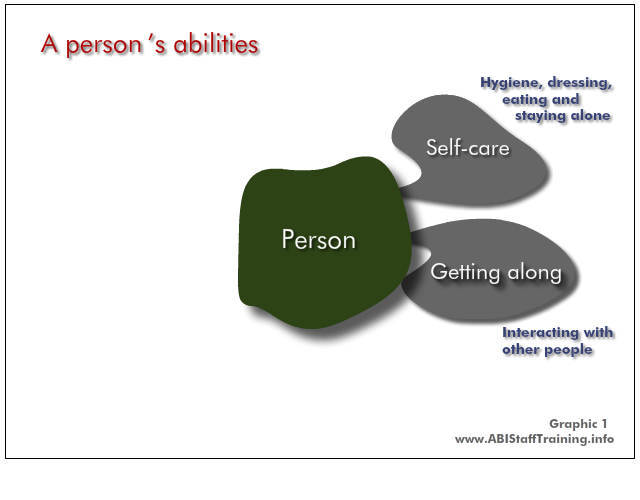
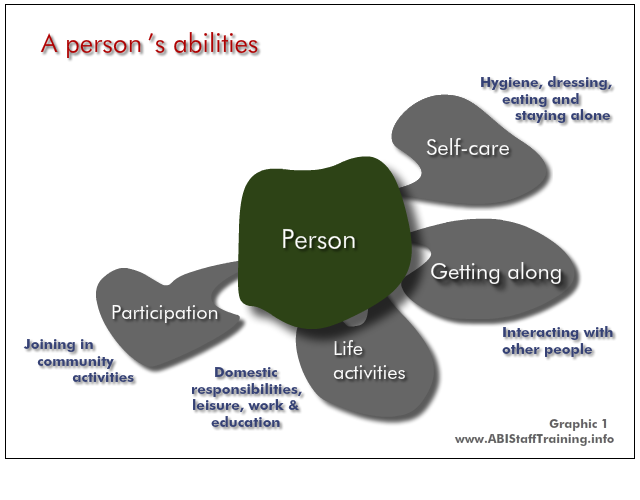
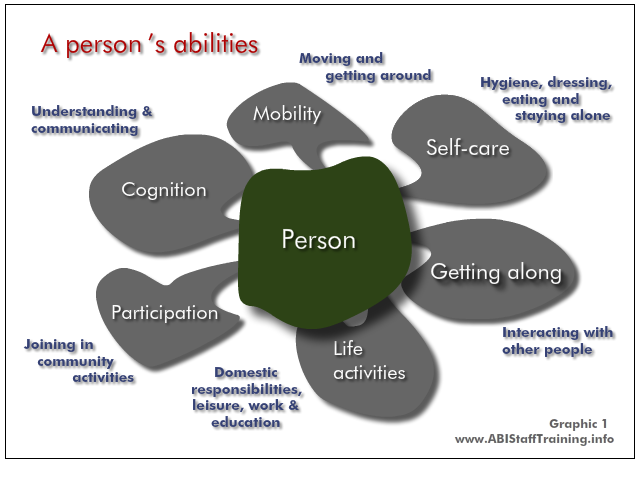
These are people's abilities. An ABI will impact on these abilities. A mental health problem will impact on these abilities.
SLIDES:
To pause: Hover mouse over slide. To continue: move mouse off slide.
To go to a specific slide: Click on slide numbers below.
The implications for the person and their life are very different depending on when the ABI occurs, and when the mental health problem occurs.
SLIDES:
To pause: Hover mouse over slide. To continue: move mouse off slide.
To go to a specific slide: Click on slide numbers below.
SLIDES:
To pause: Hover mouse over slide. To continue: move mouse off slide.
To go to a specific slide: Click on slide numbers below.
Is mental health the absence of mental illness?
Is mental illness the absence of mental health?
Check your answers here
Is mental health the absence of mental illness?